Unlock The Secrets Of The Morse Code Alphabet: Your Ultimate Guide
The world of communication has evolved dramatically, yet one system, predating the internet and even the telephone, continues to captivate and prove its enduring utility: the morse code alphabet. This unique language of dots and dashes has stood the test of time as an effective and widely used communication method, encoding text characters as short and long signals. From its telegraphic origins to its modern-day applications in amateur radio and emergency signaling, understanding the morse code alphabet opens a window into a fascinating chapter of human ingenuity and resilience.
Whether you're a beginner intrigued by its simplicity or an enthusiast looking to deepen your understanding, this comprehensive guide will walk you through the intricacies of the morse code alphabet, its rich history, and its enduring legacy. We'll explore how to read and translate this timeless code, delve into its strategic design, and even show you how to create secret messages. Prepare to embark on a journey into the world of dits and dahs!
Table of Contents
- The Enduring Legacy of the Morse Code Alphabet
- Deconstructing the International Morse Code Alphabet
- Your Comprehensive Morse Code Alphabet Chart
- Beyond English: Morse Code for Global Communication
- Learning and Practicing the Morse Code Alphabet
- Practical Applications and Secret Messages
- The Future and Enduring Relevance of Morse Code
- Conclusion
The Enduring Legacy of the Morse Code Alphabet
To truly appreciate the morse code alphabet, one must first explore its fascinating origins and the significant role it played in shaping global communication. The concept of encoding text characters as dots and dashes, or "dits" and "dahs" as they are often called, emerged in the mid-19th century. This telecommunications method was primarily developed by Samuel Morse and his assistant, Alfred Vail, for use with the electric telegraph. Their initial system, first demonstrated in the 1830s, allowed for the transmission of messages over long distances using electrical pulses.
The original Morse Code, often referred to as American Morse Code, was quite complex, featuring different lengths for the dashes and pauses, and even some unique characters. It was initially printed on paper tape as a series of indentations. However, telegraph operators soon discovered they could "read" the code by listening to the clicks of the telegraph machine, making the paper tape unnecessary. This auditory interpretation paved the way for its later adaptation to radio communications, where pulses were transmitted as short and long tones.
Interestingly, the code we primarily recognize today as the morse code alphabet only began to be widely called "Morse Code" from around the First World War. The system underwent significant improvements. In 1848, the original code was refined by the German telegraph inspector Friedrich Clemens Gerke, leading to what became known as the Hamburg Alphabet. This improved version, which standardized the lengths of dashes and pauses, laid the groundwork for the International Morse Code. This standardization was crucial for global interoperability, allowing operators from different countries to communicate seamlessly. The adoption of International Morse Code truly cemented its status as a universal communication system, transcending linguistic barriers with its simple yet powerful binary structure.
Deconstructing the International Morse Code Alphabet
So, what exactly is the morse code alphabet? At its core, Morse Code is a special way of encoding characters that encrypts alphabet letters, numbers, and punctuation using a sequence of signals—long (dashes) and short (dots). The international morse code is the standard form used worldwide, providing a consistent system for communication across various platforms.
The brilliance of the morse code alphabet lies in its strategic design. The most commonly used letters in the English language, such as 'E' (a single dot) and 'T' (a single dash), use the shortest arrangement of dots and dashes. This makes communicating in Morse Code faster and more efficient, as frequent characters require less time to transmit. It also makes memorizing these high-frequency letters significantly easier for learners. This thoughtful design contributed immensely to its practicality and widespread adoption, especially in an era where every second of transmission time counted.
When transmitted, these dots and dashes are represented by short and long electrical pulses, light flashes, or sound tones. For example, in sound, a dot is a brief tone, and a dash is a tone three times longer than a dot. The spaces between dots and dashes within a character are equal to one dot, while the space between characters is equal to three dots (one dash). The space between words is typically seven dots long. This precise timing is crucial for accurate transmission and reception, allowing messages to be decoded reliably.
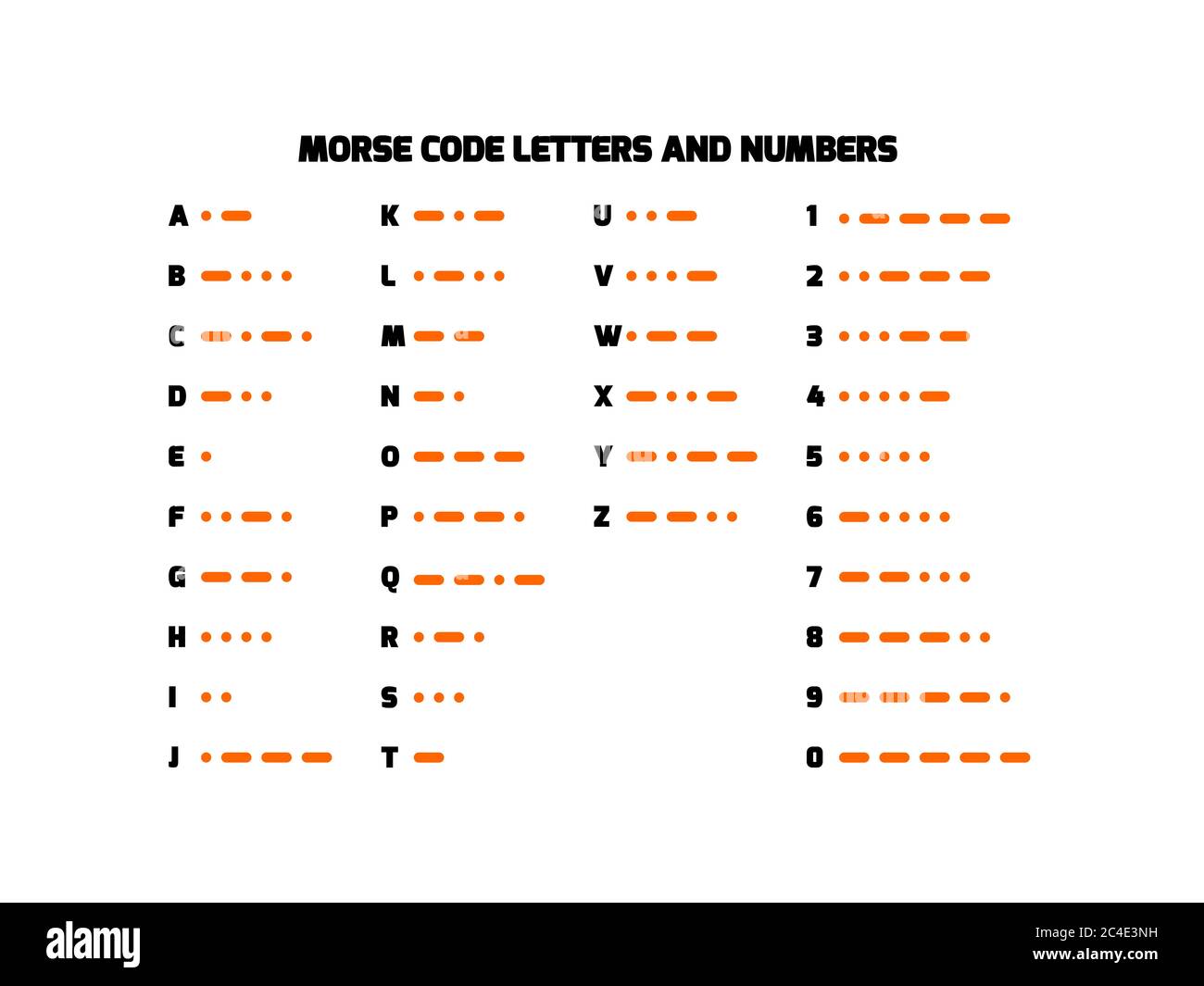
Your Comprehensive Morse Code Alphabet Chart
A morse code chart is a visual representation of the code, displaying each letter of the alphabet, numbers, and common punctuation marks alongside their corresponding Morse Code sequence. This chart is your essential tool for learning and translating Morse Code characters. The international morse code characters are standardized, ensuring global understanding.
Below, we outline the structure of this extensive alphabet chart. To truly learn the morse code alphabet, it's not just about seeing the dots and dashes, but also about understanding their sound and rhythm.
Mastering the Letters: A-Z
The international morse code alphabet consists of a table of 26 letters, which forms the core of this communication system. Each letter has a unique pattern of dots and dashes. For instance:
- A: .- (dit-dah)
- B: -... (dah-dit-dit-dit)
- C: -.-. (dah-dit-dah-dit)
- D: -.. (dah-dit-dit)
- E: . (dit)
- F: ..-. (dit-dit-dah-dit)
- G: --. (dah-dah-dit)
- H: .... (dit-dit-dit-dit)
- I: .. (dit-dit)
- J: .--- (dit-dah-dah-dah)
- K: -.- (dah-dit-dah)
- L: .-.. (dit-dah-dit-dit)
- M: -- (dah-dah)
- N: -. (dah-dit)
- O: --- (dah-dah-dah)
- P: .--. (dit-dah-dah-dit)
- Q: --.- (dah-dah-dit-dah)
- R: .-. (dit-dah-dit)
- S: ... (dit-dit-dit)
- T: - (dah)
- U: ..- (dit-dit-dah)
- V: ...- (dit-dit-dit-dah)
- W: .-- (dit-dah-dah)
- X: -..- (dah-dit-dit-dah)
- Y: -.-- (dah-dit-dah-dah)
- Z: --.. (dah-dah-dit-dit)
To truly learn the morse code alphabet, it's crucial to not just see the patterns but also to hear them. Many online resources and apps allow you to listen to the sound and pronunciation of each code, helping you internalize the rhythm. Remember, a "dit" is a short sound, and a "dah" is a sound three times longer.
Numbers and Punctuation: Completing the Language
Beyond letters, the morse code alphabet also includes codes for numbers and common punctuation marks, making it a complete communication system.
- 0: ----- (dah-dah-dah-dah-dah)
- 1: .---- (dit-dah-dah-dah-dah)
- 2: ..--- (dit-dit-dah-dah-dah)
- 3: ...-- (dit-dit-dit-dah-dah)
- 4: ....- (dit-dit-dit-dit-dah)
- 5: ..... (dit-dit-dit-dit-dit)
- 6: -.... (dah-dit-dit-dit-dit)
- 7: --... (dah-dah-dit-dit-dit)
- 8: ---.. (dah-dah-dah-dit-dit)
- 9: ----. (dah-dah-dah-dah-dit)
Common punctuation marks also have their unique dot and dash codes:
- Period (.): .-.-.- (dit-dah-dit-dah-dit-dah)
- Comma (,): --..-- (dah-dah-dit-dit-dah-dah)
- Question Mark (?): ..--.. (dit-dit-dah-dah-dit-dit)
- Slash (/): -..-. (dah-dit-dit-dah-dit)
- Equals Sign (=): -...- (dah-dit-dit-dit-dah)
- Plus Sign (+): .-.-. (dit-dah-dit-dah-dit)
Understanding the dot and dash code for each letter, number, and punctuation character in international Morse Code is fundamental. And for spaces, a specific timing interval is used rather than a character. As mentioned, a space between words is typically represented by a pause equal to seven dots. This distinct timing helps differentiate between characters and words.
Beyond English: Morse Code for Global Communication
While the morse code alphabet is most commonly associated with the Latin (English) alphabet, its universal structure allows for adaptation to various other languages and character sets. You can learn and translate Morse Code characters for different languages and punctuation marks, extending its reach far beyond its original scope.
Modern Morse Code translators and resources explore a comprehensive morse code chart featuring not only Latin but also Cyrillic, Greek, Hebrew, Arabic, Persian, Japanese (using the Wabun Code), Korean, and Thai alphabets. This adaptability underscores its power as a truly international communication system. While the underlying principles of dots and dashes remain, specific mappings or supplementary codes are developed to accommodate the unique characters and phonetic structures of these diverse languages. For instance, Japanese Morse Code (Wabun Code) is based on the kana syllabary rather than individual letters.
The ability to translate between Morse Code and these diverse alphabets is a testament to its flexibility. Modern tools, like advanced Morse Code translators, can not only convert text to Morse Code and vice-versa but also play, flash, or vibrate the Morse Code, making it accessible to different learning styles and communication needs.
Learning and Practicing the Morse Code Alphabet
Learning the morse code alphabet might seem daunting at first, but with the right approach and consistent practice, anyone can master this unique language. The key is to move beyond simply memorizing the dots and dashes and instead, internalize the sound and rhythm of each character.
Effective Learning Strategies
To effectively learn and practice the morse code alphabet, consider these strategies:
- Start with the Easiest: Begin with the shortest and most frequent characters like E (.), T (-), I (..), A (.-), N (-.), M (--). As mentioned, the strategic design of the morse code alphabet makes these easier to remember.
- Listen and Associate: Don't just look at the chart; listen to the audio representation for accurate Morse Code learning. Many learners use mnemonics or sound associations. For example, "dit-dah" for 'A' can be associated with the word "away."
- Farnsworth Method: This popular method involves sending characters at a faster speed but with longer pauses between them. This helps you recognize the character's overall sound pattern rather than counting individual dits and dahs, and then gradually reduces the spacing.
- Consistent Practice: Short, regular practice sessions are more effective than long, infrequent ones. Practice sending and receiving. Use our morse alphabet chart above to identify each letter's unique pattern and then try to replicate it.
- Practice Common Words and Phrases: Once you know individual letters, start practicing common words and phrases. This helps build fluency and context.
- How to Read Morse Code Alphabet: Reading Morse Code involves recognizing the patterns of dits and dahs, either visually (from a chart or flashing light) or audibly (from tones). The key is to differentiate between character spacing and word spacing. A single dit length pause separates dits and dahs within a character, a three-dit length pause separates characters, and a seven-dit length pause indicates a space between words.
Harnessing the Power of Morse Code Translators
A morse code translator is a convenient tool that can convert between normal text and Morse Code, making it invaluable for both learning and practical use. These tools are far more than simple conversion utilities; they offer features that enhance the learning experience:
- Text-to-Morse and Morse-to-Text: Easily convert any text message into its Morse Code equivalent, or decode a Morse Code sequence back into plain text.
- Auditory Learning: Discover the international morse code alphabet by finding each letter and number, and listen to how they sound. The translator can play the Morse Code, allowing you to internalize the rhythm and pronunciation of each character.
- Visual and Tactile Feedback: Some translators can flash the Morse Code using light or even vibrate it, providing alternative sensory inputs for learning and communication, especially useful for those with hearing impairments.
- Adjustable Speed: The speed, Farnsworth speed (character speed vs. word speed), and frequency of the sound are all fully adjustable. This allows you to start slow and gradually increase the speed as your proficiency grows.
- Shareability: You can often save the sound or share a link to use it to send messages to your friends, turning practice into an interactive and fun activity.
Using a free and easy-to-use morse code translator is an excellent way to practice the morse code alphabet and become proficient.
Practical Applications and Secret Messages
Beyond its historical significance, Morse Code still holds practical applications today, particularly in niche fields. Its primary purpose and usage now lie in amateur radio (ham radio), where it remains a reliable and efficient mode of communication, especially in challenging conditions. Many amateur radio operators continue to use Morse Code for its clarity and ability to cut through noise where voice communication might fail. It's also used in some emergency signaling scenarios, such as maritime distress signals.
Understanding common words, phrases, and letters used in international Morse Code is vital for these applications. The most famous example is the SOS signal (…---…), universally recognized as a distress call. This signal is designed to be easily distinguishable and memorable, making it effective in critical situations. Learning how to say "I love you" in Morse Code (.. .-.. --- ...- . -.-- --- ..-) can also be a fun and personal way to use the code.
Moreover, the morse code alphabet offers a unique way to create secret messages to send to friends online, e.g., on WhatsApp or Instagram. It adds an element of intrigue and exclusivity to your communication, turning simple text into a coded puzzle. This playful application keeps the code relevant and engaging for a new generation.
The Future and Enduring Relevance of Morse Code
While the morse code alphabet is no longer the primary means of global communication, its legacy is undeniable. It laid the foundation for modern telecommunications and continues to serve as a testament to human ingenuity in overcoming communication barriers. Its simplicity, robustness, and efficiency in low-bandwidth conditions ensure its continued relevance in specific domains like amateur radio and emergency preparedness.
The enduring fascination with Morse Code also speaks to a human desire for alternative forms of expression and connection. Whether for historical interest, a hobby, or practical application in niche fields, the ability to understand and utilize this unique language of dots and dashes remains a valuable and rewarding skill. It reminds us that even in an age of instant digital communication, the fundamental principles of encoding and decoding information remain timeless.
Conclusion
The morse code alphabet is much more than just an antiquated communication system; it's a testament to human innovation, a foundational element of telecommunications history, and a fascinating skill to acquire. We've explored its origins, understood the strategic design of its international standard, delved into comprehensive charts for letters, numbers, and punctuation, and even touched upon its global adaptability.
Learning the morse code alphabet is an engaging journey that hones your auditory and cognitive skills. With the aid of charts, practice, and modern translators, mastering this unique language of dots and dashes is more accessible than ever. Whether you're aiming to communicate with amateur radio enthusiasts, send intriguing secret messages to friends, or simply appreciate a pivotal piece of communication history, the morse code alphabet offers a rewarding experience.
What are your thoughts on Morse Code? Have you ever tried to learn it, or do you know someone who uses it? Share your experiences and questions in the comments below! If you found this guide helpful, consider sharing it with others who might be curious about this timeless communication method. Explore more articles on our site to continue your journey through the fascinating world of communication technologies.
- Katmoviehd Com
- Yolo Lary Porn
- Cathy White And Blue Ivy Comparison
- Kris Fade Daughters Adopted
- Movierlz

Morse Code Alphabet

Printable Morse Code Alphabet
International Morse Code Alphabet. Set of encoded letters and numbers